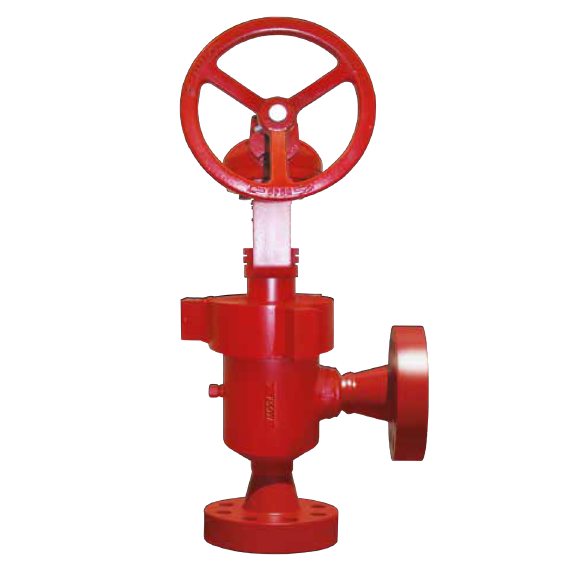
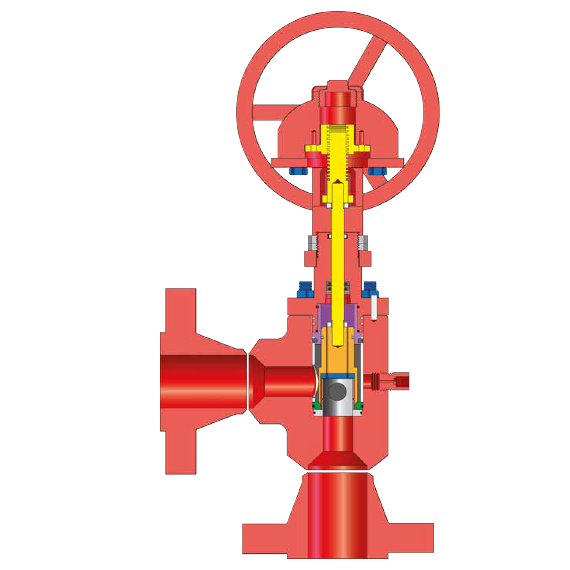
The RB Series Control Valve features several unique design characteristics that minimize wear and maximize service life.
The nozzle and external sleeve trim is designed to contain turbulence and wear by managing the flow into the nozzle and centralizing it into bore causing the flow streams to impinge on each other. The valve body and outlet are protected from wear because the energy conversion as a result of the pressure drop is concentrated in the trim cavity before flow enters the outlet. This eliminates the typical wear problems in the valve outlet. The Upstream and Downstream balanced sleeve design greatly reduces the breakway and closing thrust requirements to lift the sleeve on and off seat as well as during stem travel making the control stable and precise yielding better accuracy and repeatability.